LEAP iteratively fine-tunes LLM agents using on-policy feedback from privileged AI teachers.
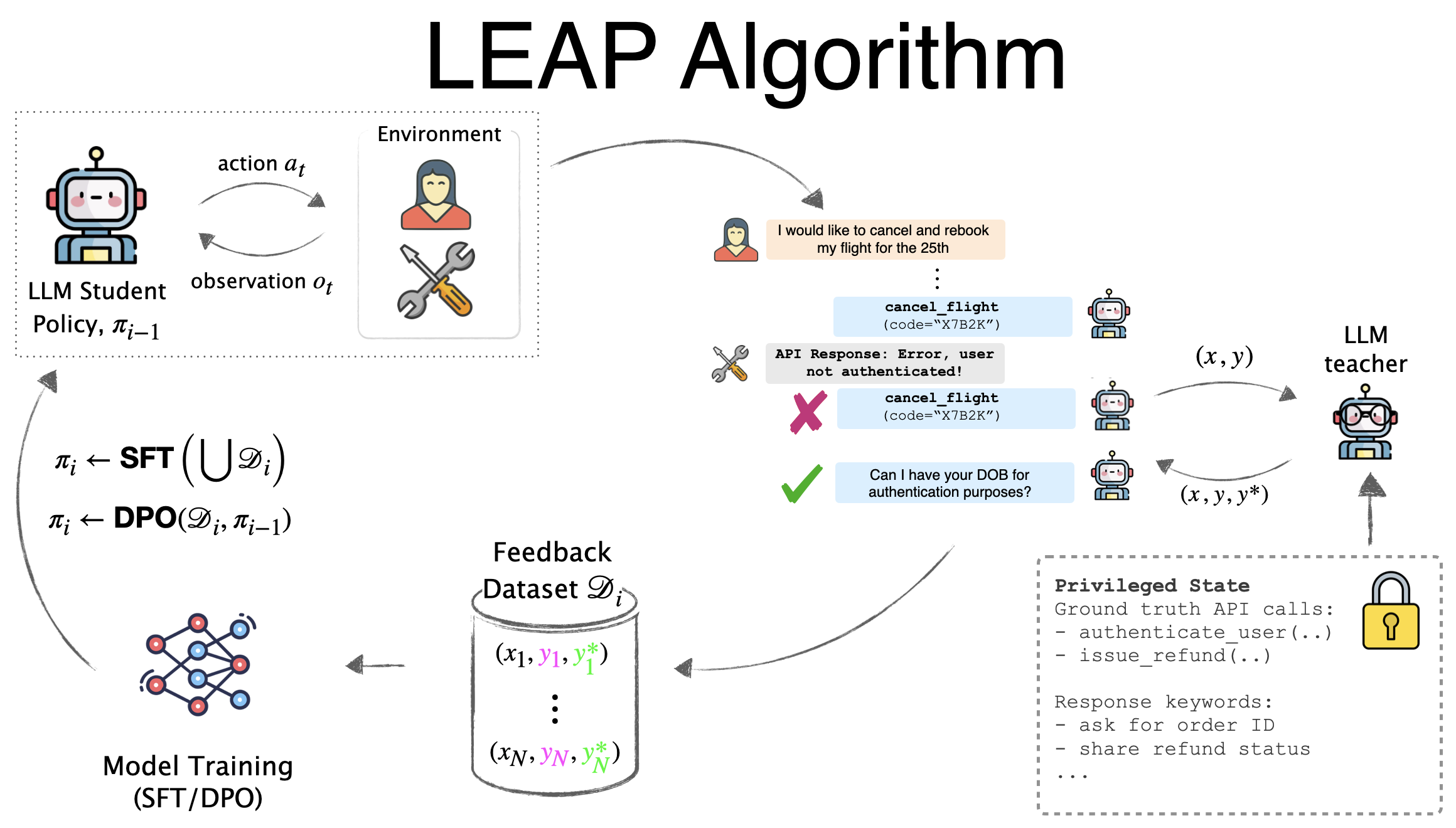
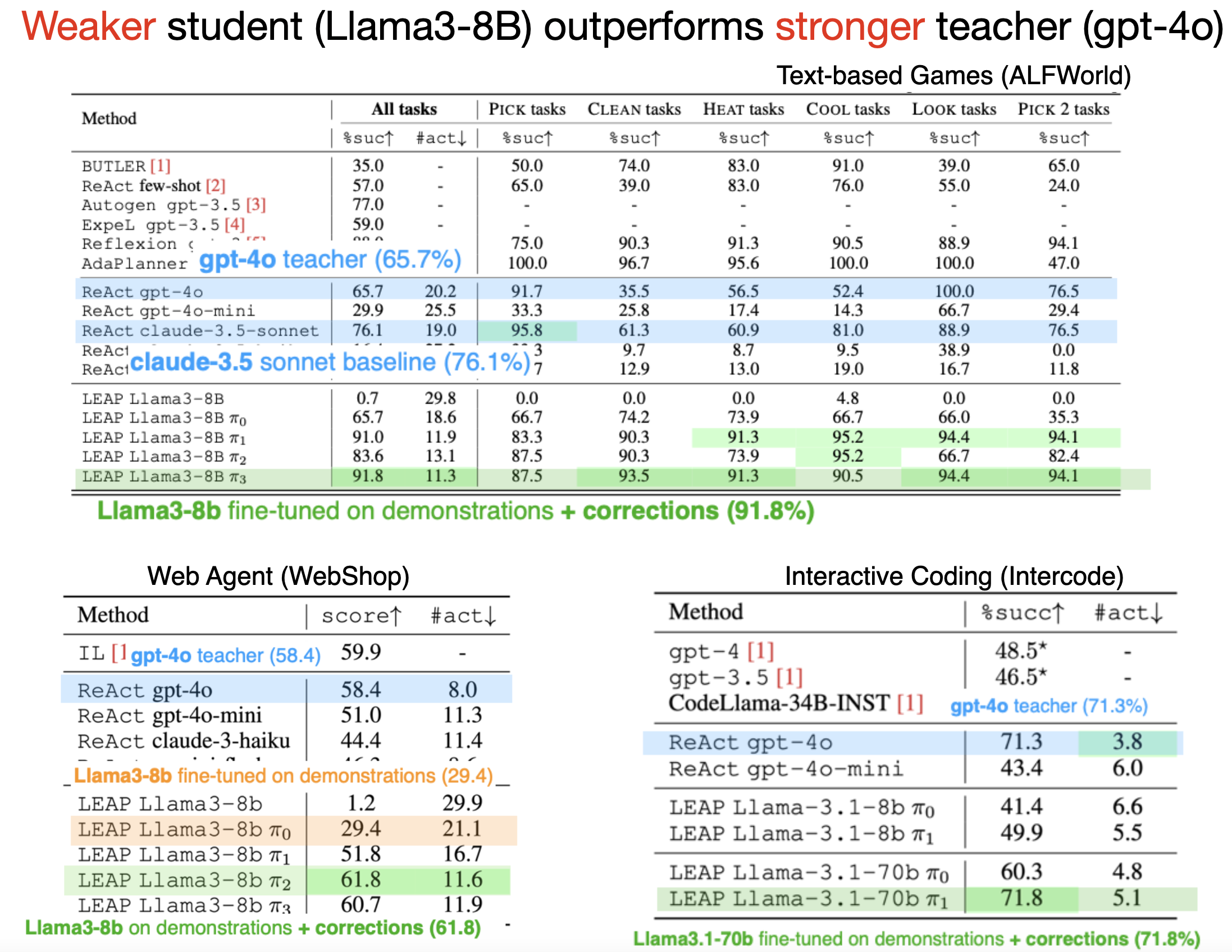
While large language models (LLMs) show impressive decision-making abilities, current methods lack a mechanism for automatic self-improvement from errors during task execution. We propose LEAP, an iterative fine-tuning framework that continually improves LLM agents using feedback from AI expert teachers. Our key insight is to equip the expert teachers with a privileged state -- information available during training but hidden at test time. This allows even weak experts to provide precise guidance, significantly improving the student agent's performance without access to privileged information at test time. We evaluate LEAP on diverse decision-making benchmarks, including text-based games, web navigation, and interactive coding. Our experiments show that LEAP (1) outperforms state-of-the-art baselines (2) enables weak student models (e.g., Llama3-8B) to exceed the performance of strong teacher models (GPT4-o), and (3) allows weak models to self-improve using privileged versions of themselves. We also provide a theoretical analysis showing that LEAP's success hinges on balancing privileged information with the student’s realizability, which we empirically validate.
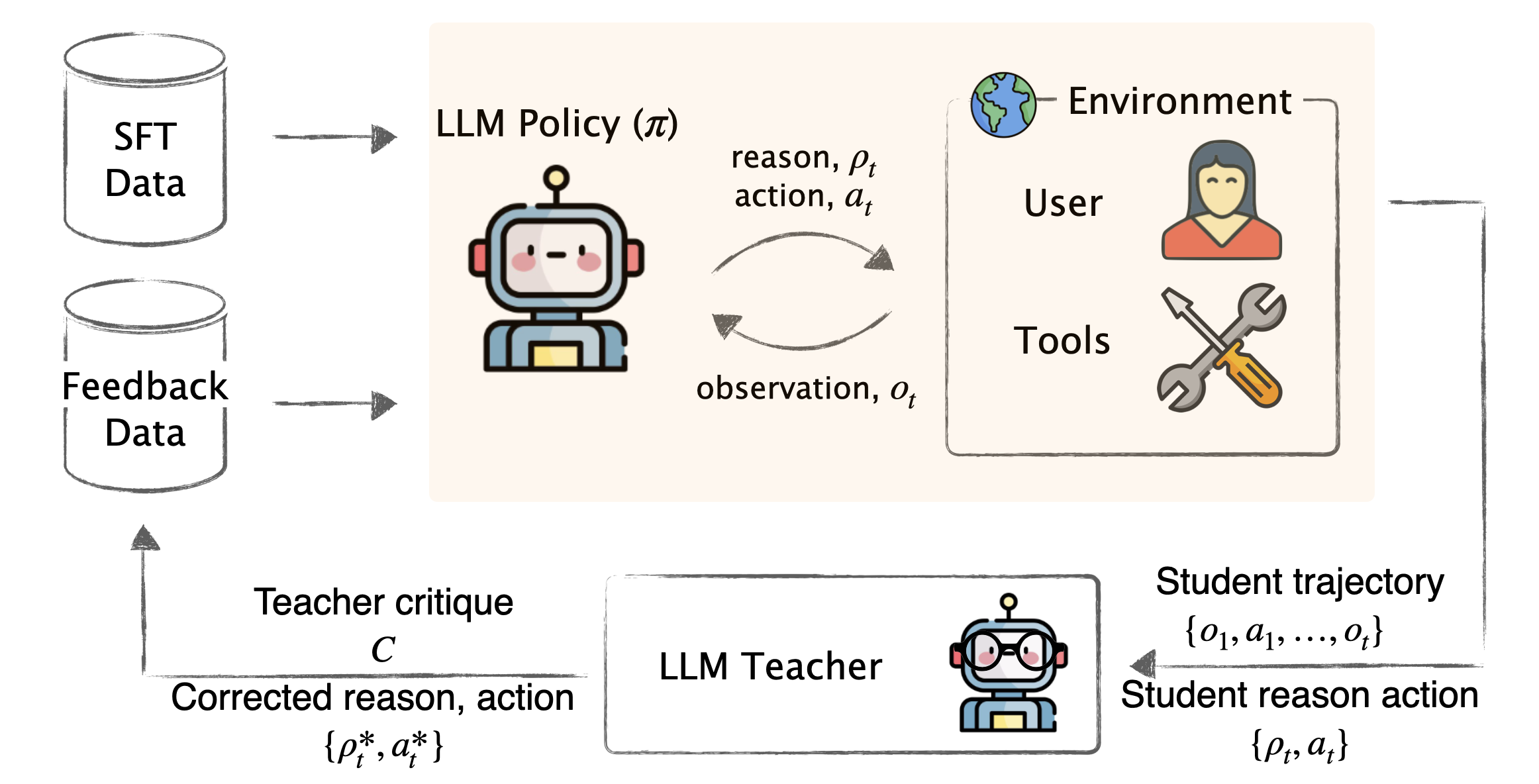
Challenge: How can LLM teacher compute optimal corrections?
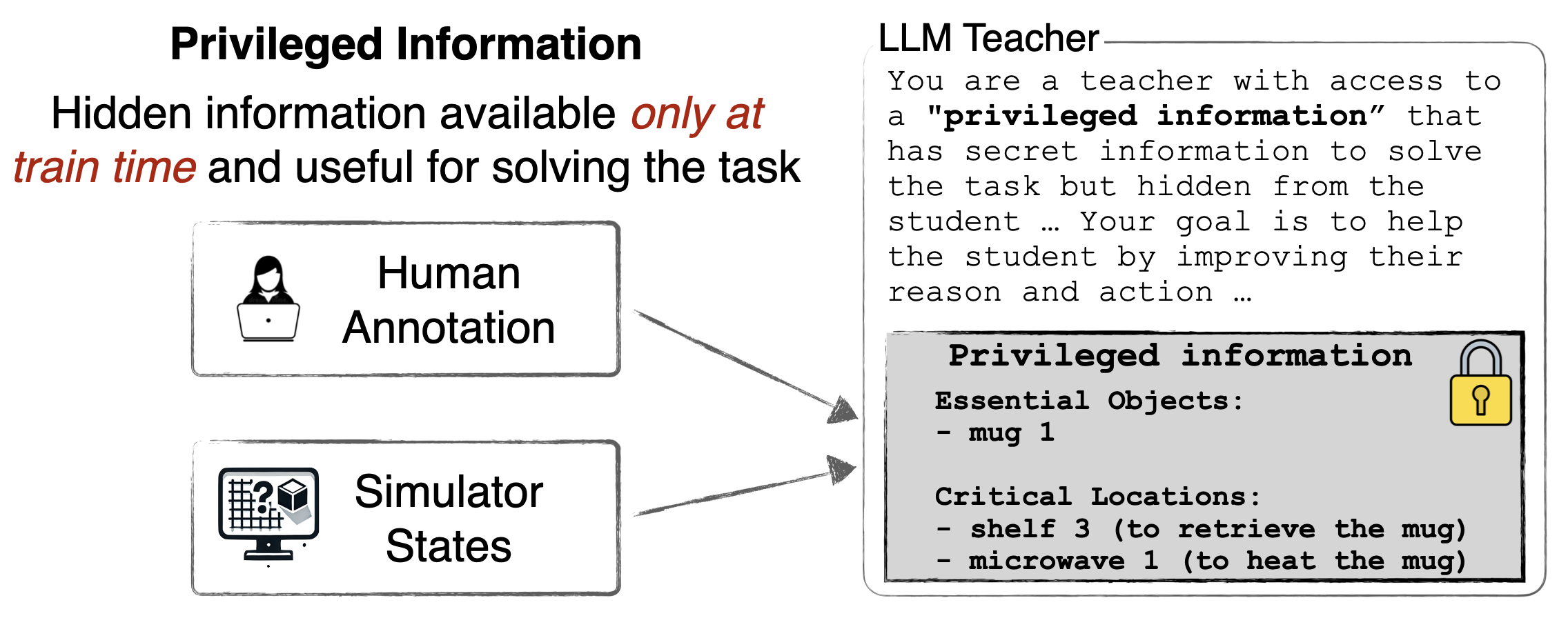
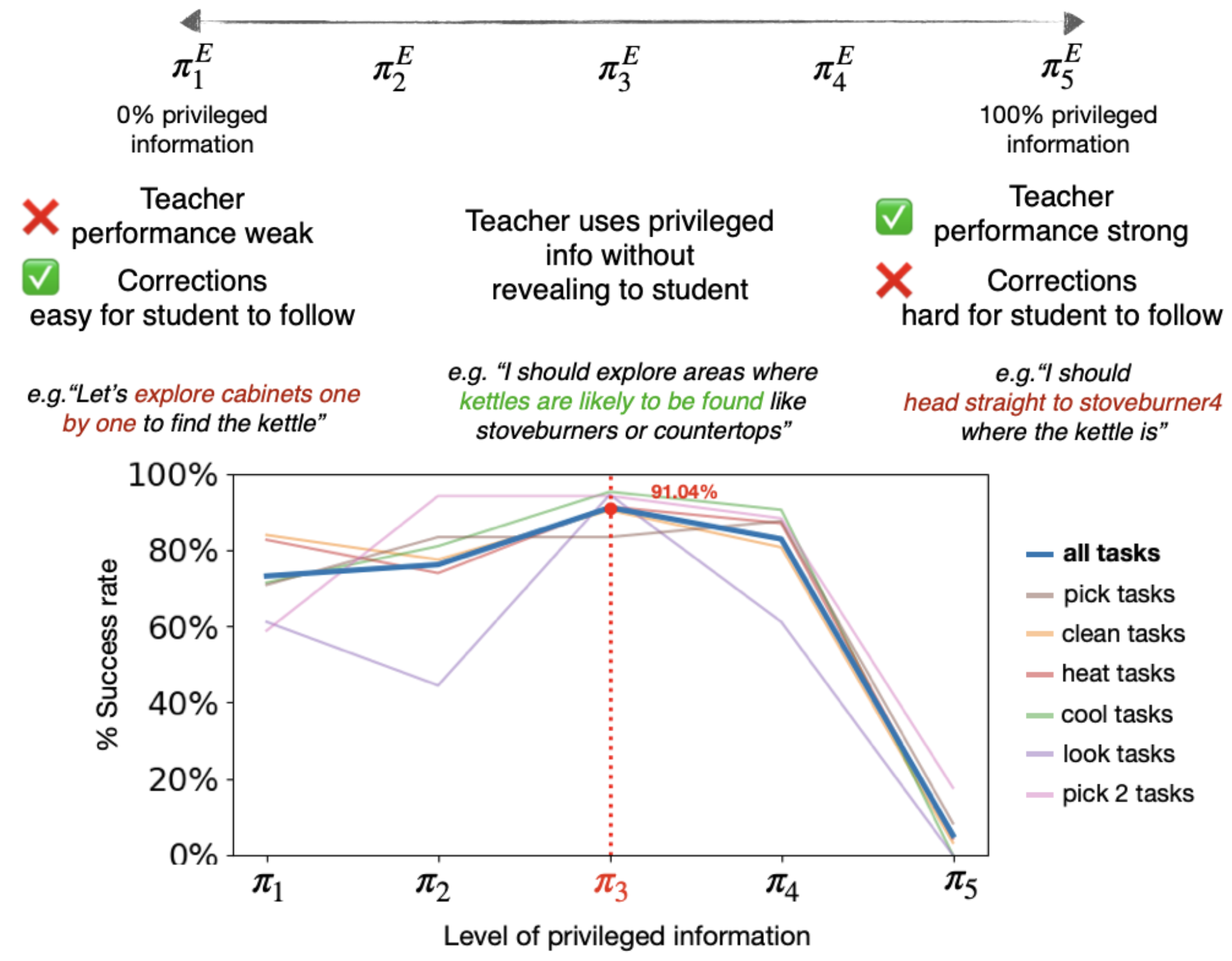
Hypothesis 1: LEAP balances privileged information with realizable corrections
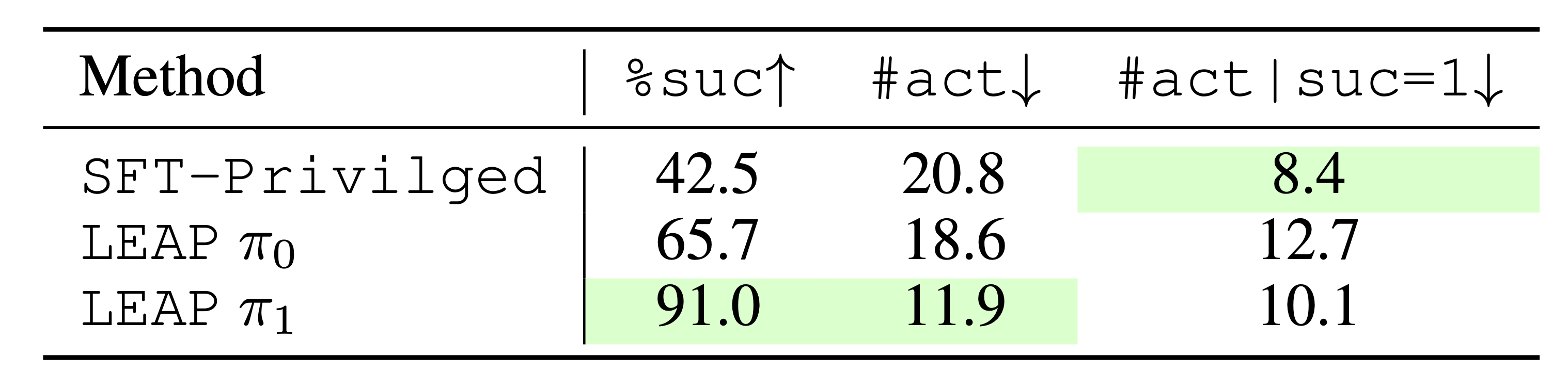
Hypothesis 2: LEAP provides on-policy corrections
@inproceedings{choudhury2024better,
title={Better than Your Teacher: LLM Agents that learn from Privileged AI Feedback},
author={Choudhury, Sanjiban and Sodhi, Paloma},
booktitle={International Conference on Learning Representations (ICLR)}
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2410.05434},
year={2025}
}